On this page
Interaction Code grant type
Identity EngineOverview
Okta has introduced an extension to the OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect standard called the Interaction Code grant type. This grant type enables you to create a more customized user authentication experience.
The Interaction Code grant type allows native, SPA, and web apps to manage user interactions with the authorization server directly, instead of relying on a browser-based redirect to an authentication component, such as the Okta Sign-In Widget. This direct interaction is useful when the client app wants to interact directly with the user and doesn’t need to share an authenticated session with other apps.
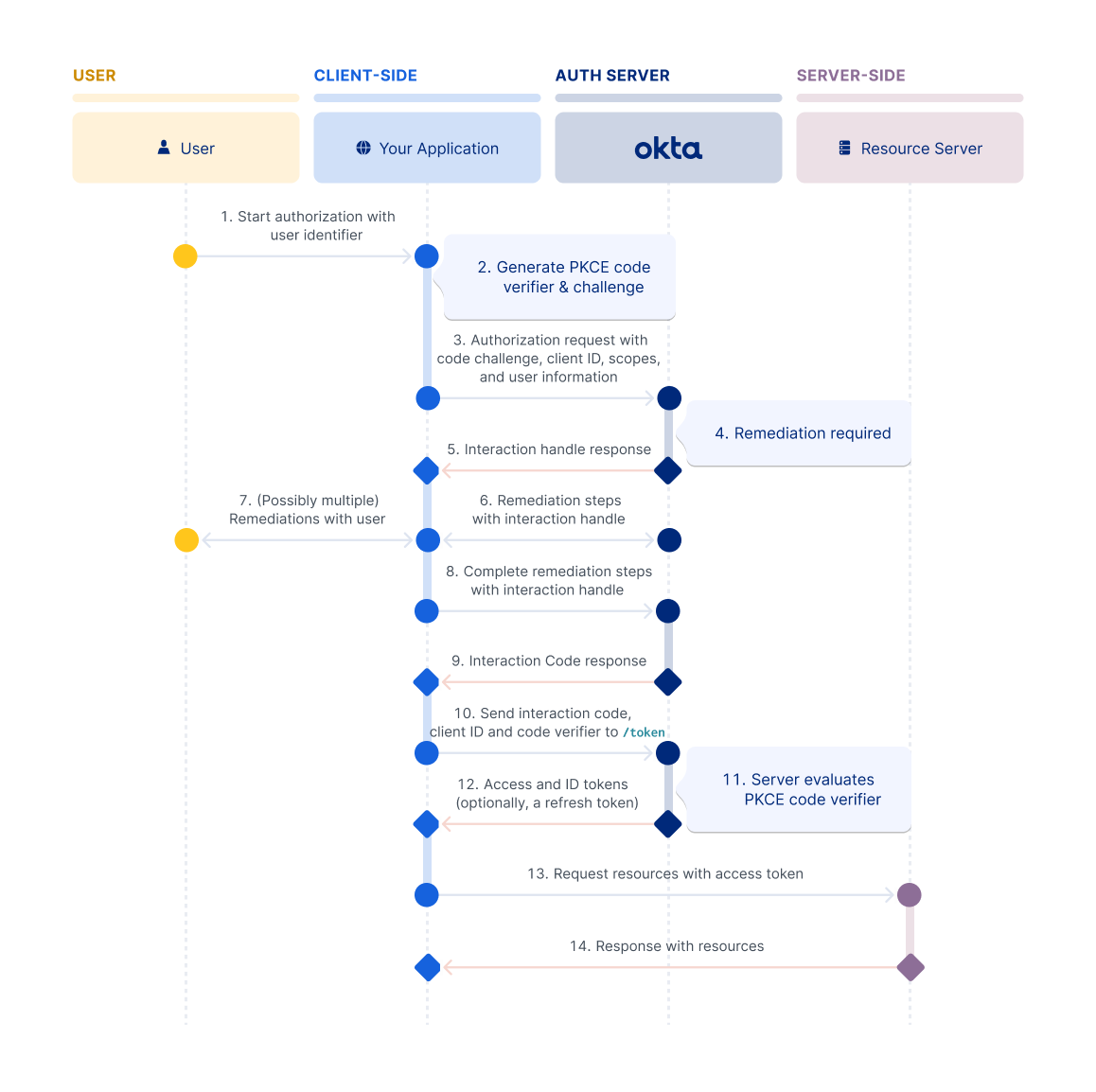
The Interaction Code flow consists of a series of interactions between the user and the authorization server, facilitated by the client. Each interaction is called a remediation step and corresponds to a piece of user data required by the authorization server. The client obtains these remediation steps from the Identity Engine component of the Okta authorization server. The client then prompts the user for the required data at each step to continue the flow.
Each step of the remediation is a criterion of assurance for authenticating the user. Also, each step is evaluated at runtime based on predefined Okta authorization server and app sign-in policies. The number and nature of remediation steps are configurable in the policies with minimal disruption to the running app. This allows the authentication experience to differ based on user, group, context, app, available factors, and so on.
Remediation
Remediation is the direct communication between the client and Identity Engine. You can achieve this direct communication either without a browser redirect or with a browser redirect when the remediation transitions through a push authorization request.
For example, a user could start an authentication flow by entering only a username, and this would prompt the client to request more information, or remediation, as required. A follow-up remediation step might involve the client prompting the user for a password or to add a second factor. Then, that information is sent directly to the Identity Engine for verification.
Each form of remediation that the user must supply is dictated by the evaluated policies between the Okta authorization server and the app. When the remediation steps are complete, the Identity Engine component provides the client with an Interaction Code that the client can exchange for tokens by an Okta authorization server. This exchange follows the OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect standards.
The Interaction Code grant is intended for developers who want to control the step-by-step remediation user experience without using a web browser to redirect authentication. This grant type enables developers to include Identity Engine features (opens new window) in their app, such as passwordless authentication and progressive profiling.
The Interaction Code flow can use policy-driven remediation steps not only for authentication, but also for registration and account recovery. See Okta deployment models—redirect vs. embedded for the different deployment models. Also, see the embedded authentication use cases linked in the Identity Engine deployment guides for detailed Interaction Code flow implementations.
The Interaction Code flow
The Interaction Code flow is similar to the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code flow with PKCE. All clients are required to pass a client ID, and a Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE), to keep the flow secure. Confidential clients such as web apps must also pass a client secret in their authorization request.
The user can start the authorization request with minimal information, relying on the client to facilitate the interactions with the Identity Engine component of the Okta authorization server to progressively authenticate the user. The series of interactions is managed using the interaction_handle, which acts as a state handle for each transaction. After successfully completing the remedial interactions, the client receives an interaction_code that they can redeem for tokens from an Okta authorization server with the /token (opens new window) endpoint.
The following Okta authorization server types support the Interaction Code flow: the org authorization server and the custom authorization server. These Okta authorization servers must have the Interaction Code grant type configured to accept Interaction Code requests.
The following table describes the parameters introduced for the Interaction Code grant type flow:
| Interaction Code grant parameter | Description |
|---|---|
interaction_handle | The interaction_handle is an opaque, immutable value that is provided by the Identity Engine component of an Okta authorization server. The client can use the interaction_handle to interact with the Identity Engine component directly. The client is responsible for saving the interaction_handle and using it to hold the state of the transaction during remediation. Any public/confidential client that is configured to use the Interaction Code grant type can obtain an interaction_handle. If all the remediation steps are successfully performed, an interaction_code is returned as part of the success response. |
interaction_code | The interaction_code is a one-time use, opaque code that the client can exchange for tokens using the Interaction Code grant type. This code enables a client to redeem a completed Identity Engine interaction for tokens without needing access to an authorization server’s session. |
The following sequence of steps is a typical Interaction Code flow: