On this page
SAML assertion inline hook
This guide provides a useable example of an Okta SAML assertion inline hook. It uses the website Glitch.com (opens new window) to act as an external service to receive and respond to SAML assertion inline hook calls.
Learning outcomes
- Understand the Okta SAML assertion inline hook calls and responses.
- Implement a simple functional example of a SAML assertion inline hook with a Glitch.com Node.js external service.
- Preview and test the SAML assertion inline hook.
Note: The Glitch project referenced in this guide is no longer available due to the end of Glitch web hosting. Okta is revising this guide to use another tool or site. See Event hooks with ngrok and the ngrok utility as another way to demo Okta hooks or products.
What you need
- Okta Integrator Free Plan org (opens new window)
- Glitch.com (opens new window) project or account
- A sample app that uses SAML to implement authentication. This guide works with the app in the Sample code section that follows.
Sample code
- Okta SAML assertion inline hook example
- Spring Boot, SAML, and Okta (opens new window)
About SAML assertion inline hook implementation
Use the SAML assertion inline hook to customize the authentication workflow that occurs between an app and the Okta org. The Okta org functions as the Identity Provider (IdP).
This guide provides an end-to-end scenario that uses a SAML-authenticated app and an Okta org. It includes example code for an external service to respond to calls from a SAML assertion inline hook that's triggered during the authentication workflow.
The scenario
Consider a scenario where the external service code parses a request from Okta and evaluates the user name against a simple patient data store. If the user is part of the patient store, the external service responds to Okta with a command to add a patient ID claim to the SAML assertion. Otherwise, if the username isn't part of the data store, no action is taken.
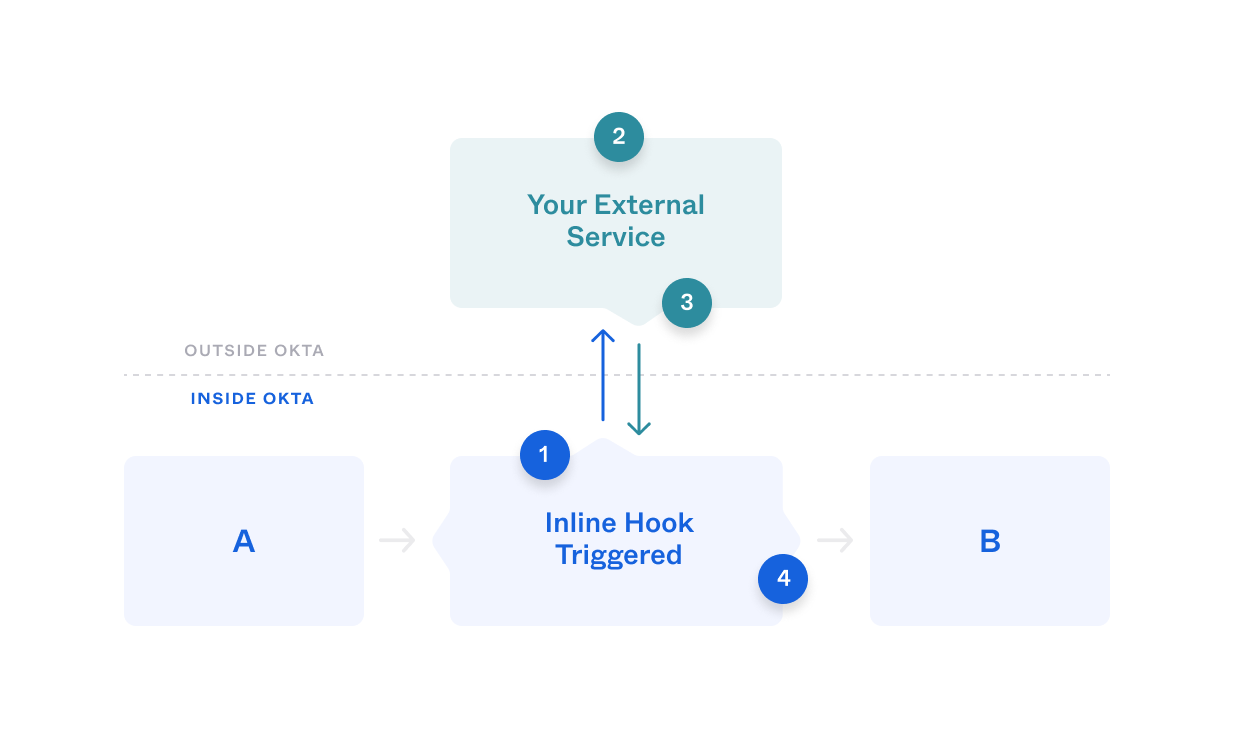
At a high-level, the following workflow occurs:
- A user signs in to an app authenticated by SAML, which uses the Okta org as an Identity Provider (IdP), and authenticates the user (A).
- At this point in the workflow, the Okta SAML assertion inline hook triggers (1) and sends a request to an external service.
- The external service evaluates the request (2). If the user exists in the patient data store, the service sends a response to Okta to include the patient's ID in the assertion (3).
- The user is signed in to the app with the additional claim in the SAML assertion (B).
Set up the sample SAML-authenticated app
The Spring Boot, SAML, and Okta app is designed to implement SSO with Spring Security's SAML and Okta.
Access the Spring Boot, SAML, and Okta code from the following GitHub repository:
https://github.com/oktadev/okta-spring-boot-saml-example (opens new window)
See Get Started with Spring Boot and SAML (opens new window), a blog post by developer advocate Matt Raible, for background and instructions on setting up this app.
Or follow the README (opens new window) instructions to install and run the Spring Boot sample app with your Okta org.
Make sure to have this app running before proceeding with the SAML assertion inline hook setup.
Create the external service code
You can now create the external service code that resides on your third-party site (in this example, the Glitch.com site). The third-party site receives and responds to the SAML assertion inline hook call from Okta. The responses to the SAML assertion inline hook call can customize the SAML assertion in multiple ways, including adding or replacing elements of the assertion.
In this example code, a new claim is added to the assertion. For further information on the SAML assertion commands object and how you can modify the assertion, see the SAML assertion inline hook reference (opens new window) documentation.
To run the scenario immediately, copy (remix) the Glitch.com project code for the Okta SAML assertion inline hook example. Skip to the Activate and enable the SAML assertion inline hook section to configure the SAML inline hook.
Note: Ensure that you have the required default code and packages in your sample project. See Common hook set-up steps.
Note: The sample application uses Basic Authentication. Ensure that you add the authentication credentials to the environment variables in the sample application's
.envfile. See HTTP Basic Authentication.
You might want to create the external service yourself. If so, use the following sections that detail a portion of the code that parses the SAML assertion inline hook call, checks the data store, and then responds to Okta.
Note: Ensure that you modify the project code's data store with a user that belongs to your org.
Parse the SAML assertion inline hook
The external service in this scenario requires code to handle the SAML assertion inline hook request from the Okta org. Use the Glitch example to either build or copy the code (remix on Glitch) that parses the SAML assertion inline hook call.
Note: Make sure to have the required default code and packages in your Glitch project. See Common Hook set-up steps.
From the SAML assertion inline hook request, the code retrieves the name of the user who is authenticating from the data.context.user object.
The following Node.js code parses the Okta request body for the username and email address, and stores the email address in the variable patientName.
//Inline SAML Hook POST from Okta (endpoint: SAMLHook)
app.post("/SAMLHook", (request, response) => {
console.log(" ");
console.log("User email: " + request.body.data.context.user.profile["login"]);
console.log("Name: " + request.body.data.context.user.profile["firstName"] + " " + request.body.data.context.user.profile["lastName"]);
var patientName = request.body.data.context.user.profile["login"];
...
});
Check against the data store
In this scenario, a pre-populated static array of patient names and patient IDs (patients) is used to simulate a real-world data store. The user email address included with the Okta request is checked against this array. If the user in the request matches a value in the patient's array, the associated patient ID is stored as a variable, patientID.
Note: Modify this data store to make sure it contains one or more users that are assigned to your app in your Okta org.
The following Node.js code checks the username against the data store:
// Example Patients Data Store
const patients = [
{
username: 'michelle.test@example.com', // Update one of these username values to a user in your org.
ExternalServicePatientID: '1235',
},
{
username: 'bob.uncle@example.com',
ExternalServicePatientID: '6789',
},
{
username: 'mark.christie@example.com',
ExternalServicePatientID: '4235',
},
]
//Inline SAML Hook POST from Okta (endpoint: SAMLHook)
app.post("/SAMLHook", (request, response) => {
console.log(" ");
console.log("User email: " + request.body.data.context.user.profile["login"]);
console.log("Name: " + request.body.data.context.user.profile["firstName"] + " " + request.body.data.context.user.profile["lastName"]);
var patientName = request.body.data.context.user.profile["login"];
if (patients.some(user => user.username == patientName)){
const arrayPosition = patients.findIndex(user => user.username == patientName);
const patientID = patients[arrayPosition].ExternalServicePatientID;
...
}
});
Send a response to Okta
The variable, patientID, can now be returned to Okta as an additional SAML assertion claim using the commands object:
{ "commands":[
{ "type":"com.okta.assertion.patch",
"value": [
{
"op": "add",
"path": "/claims/extPatientId",
"value": {
"attributes": {
"NameFormat": "urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:unspecified"
},
"attributeValues":[
{
"attributes": {
"xsi:type": "xs:integer"
},
"value": patientID,
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
For further information on the SAML assertion commands object, see the SAML assertion inline hook reference (opens new window) documentation.
The following Node.js code adds the commands object, returns the response to Okta, and completes the sample code:
//Inline SAML Hook POST from Okta (endpoint: SAMLHook)
app.post("/SAMLHook", (request, response) => {
console.log(" ");
console.log("User email: " + request.body.data.context.user.profile["login"]);
console.log("Name: " + request.body.data.context.user.profile["firstName"] + " " + request.body.data.context.user.profile["lastName"]);
var patientName = request.body.data.context.user.profile["login"];
if (patients.some(user => user.username == patientName)){
const arrayPosition = patients.findIndex(user => user.username == patientName);
const patientID = patients[arrayPosition].ExternalServicePatientID;
var returnValue = { "commands":[
{ "type":"com.okta.assertion.patch",
"value": [
{
"op": "add",
"path": "/claims/extPatientId",
"value": {
"attributes": {
"NameFormat": "urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:unspecified"
},
"attributeValues":[
{
"attributes": {
"xsi:type": "xs:integer"
},
"value": patientID,
}
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
console.log("Added patient ID claim to SAML assertion: " + returnValue.commands[0].value[0].value.attributeValues[0]["value"]);
response.send(JSON.stringify(returnValue));
}
else {
console.log("Not a patient. No change to SAML assertion.");
response.status(204).send();
}
}
);
Activate and enable the SAML assertion inline hook
Activate and enable the SAML assertion inline hook within your Admin Console.
Activating the SAML assertion inline hook registers the hook with the Okta org and associates it with your external service. Enabling the SAML assertion inline hook associates the hook with your SAML app.
Activate the SAML assertion inline hook
Go to the Workflow > Inline Hooks page.
Click Add Inline Hook and select SAML from the dropdown menu.
Add a name for the hook (in this example, "Patient SAML Hook").
Add your external service URL, including the endpoint. For example, use your Glitch project name with the endpoint:
https://your-glitch-projectname.glitch.me/SAMLHook.Add the Authentication field and Authentication secret values. This example uses HTTP Basic Authentication.
- Authentication field =
authorization - Authentication secret =
Basic YWRtaW46c3VwZXJzZWNyZXQ=
Note: If you want to use OAuth 2.0 to secure your inline hooks, see OAuth 2.0: Client Secret or OAuth 2.0: Private Key.
- Authentication field =
Click Save.
The SAML assertion inline hook is now set up with a status of active.
Enable the SAML assertion inline hook
Go to Applications and select your SAML app (in this example, "Spring Boot SAML").
Click General.
From the SAML Settings tile, click Edit.
Click Next to get to the Configure SAML tab.
From the SAML Settings tile, under the General heading, click Show Advanced Settings.
In the Assertion Inline Hook field, select your registered inline hook from the dropdown menu (in this example, "Patient SAML Hook").
Click Next and Finish.
The SAML assertion inline hook is now ready for triggering when a user authenticates through the SAML app.
Preview and test the SAML assertion inline hook
The SAML assertion inline hook is ready for preview and testing. You now have the following configured:
- The SAML app (okta-spring-boot-saml-example) is ready to sign in and authenticate users using your Okta org as an IdP.
- The external service (okta-inlinehook-samlhook) is ready with code to receive and respond to an Okta SAML assertion inline hook call.
- The Okta org is set up to call and receive a response from the external service. This occurs when a user signing in from the SAML app triggers a SAML assertion inline hook.
Preview the SAML assertion inline hook
Go to Inline Hooks (Workflow > Inline Hooks) in your Admin Console.
Click the SAML assertion inline hook name (in this example, "Patient SAML Hook").
Click Preview.
Under Configure Inline Hook request, define a value for
data.userProfileby selecting a user in your org from the data.userProfile dropdown list.Select your SAML app by typing in the Select a SAML app field (in this example, "Spring Boot SAML"), and selecting your app.
From the Preview example Inline Hook request block, click Generate Request. You should see the user's request information in JSON format that is sent to the external service.
Note: You can also Edit this call for development or testing purposes.
From the View service's response block, click View Response. A response appears from your external service in JSON format, which either adds a claim to the SAML assertion or doesn't.
Test the SAML assertion inline hook
Start your SAML app by going to your project folder (
okta-spring-boot-saml-example >) and then running the app (> ./gradlew bootRun).Go to your sample app (
http:/localhost:8080).Go to your Glitch.com project and make sure that it's listening for requests by opening the Console Logs window (Tools > Logs).
Return to your SAML app and sign in with an Okta user who isn't in the data store of patients.
The user should sign in with their username and password. After authentication, the first name, last name, email, and group attributes display on the Welcome page. In the Glitch log window, a message appears stating that the user isn't part of the data store.
Sign out of the sample app and now sign in with an Okta user who is in the data store of patients.
The user should sign in with their username and password. After authentication, the user's attributes display on the Welcome page, as before, and now include the patient ID attribute. In the Glitch log window, a message appears stating that the patient ID number was added to the SAML assertion.
Next steps
Review the following guides to implement other inline or event hook examples:
- Event hook
- Password import inline hook
- Token inline hook
- Telephony inline hook
- Registration inline hook
See also
For a complete description of this inline hook type, see the SAML assertion inline hook (opens new window) reference.