On this page
Establishing a SSL/TLS Session
When an SSL/TLS connection needs to be made between a client (a browser, or an application attempting to access an API) and a server (a web server, for example, or an API endpoint) it follows a number of steps. The TLS spec, published by the IETF Transport Layer Security Working Group, gives an overview of these steps.
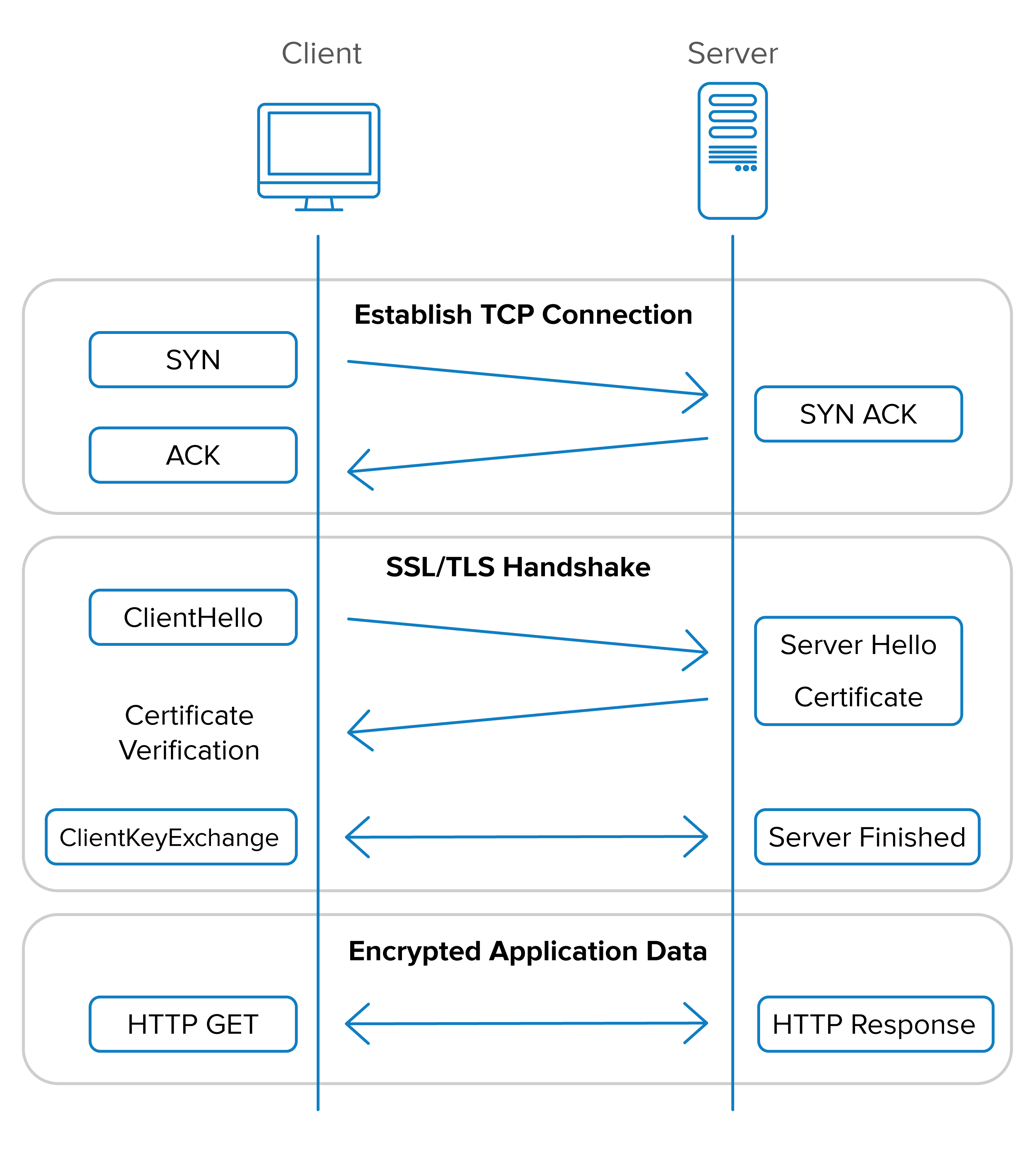
In we show a visual representation of how the client or "sender" and server or "receiver" set up an SSL/TLS connection.
Let's walk through the steps at a high level:
TCP Connection
Your client (browser or application) will initiate a TCP connection with the server. Your client and server can exchange information once this connection is established. Although TLS can work over different transports, by far the most common use case is over TCP/IP, due to its ubiquity, reliability of transport and ability to recover from lost packets and transport errors. In the diagram, SYN, SYN ACK, and ACK denote this sequence of events.
SSL/TLS Handshake
The SSL/TLS handshake takes place once a TCP connection is established.
ClientHello
The client sends a "ClientHello" message, which lists the versions of SSL/TLS the client is capable of, what ciphersuites it has available, and any compression types available.
**ServerHello and Certificate Response**The server responds with the same information as the client, and sends the server's certificate back to the client as well.
Certificate Verification
The client verifies that the certificate is valid, and also verifies that the server is authentic and not an impersonator conducting a man-in-the-middle attack. For more information about how certificate verification is accomplished, see "SSL/TLS Certificate Verification" later in this chapter.
ClientKeyExchange
In the previous section, we discussed key exchange, with the example Diffie–Hellman algorithm. This is the step of the handshake where the key exchange actually happens.
Finished/Application Data
Now that the handshake has been established and keys have been exchanged, information may be encrypted and decrypted between the client and server based on the shared secret which has been generated. This symmetric cryptography will secure the remainder of application-to-application communication.